What is the Difference Between Gout and Bunions?
Gout and bunions are common foot conditions that can cause significant discomfort and impact daily activities, yet many people struggle to distinguish between the two. While both affect the foot, their causes, symptoms, and treatments differ markedly, making accurate diagnosis crucial for effective management. In this blog, we’ll explore the key differences between gout and bunions, providing you with the essential knowledge to identify and seek appropriate treatment for these distinct conditions.
What is Gout
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, redness, and tenderness in joints, often affecting the base of the big toe. This condition is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood, leading to the formation of urate crystals in the joints, which trigger the painful symptoms. Lifestyle factors, such as diet and alcohol consumption, play a significant role in managing gout, with a focus on avoiding foods high in purines to prevent future attacks. Understanding the symptoms and causes of gout is crucial for effective treatment and management, emphasizing the importance of a proactive approach to healthcare and lifestyle adjustments.
What are Bunions
Bunions are bony protrusions that form at the base of the big toe, causing the toe to shift towards the others, which leads to a noticeable bump on the side of the foot. This condition often results in discomfort or pain, especially when wearing tight-fitting shoes or during prolonged periods of walking or standing. While genetics play a pivotal role in the development of bunions, factors like improper footwear and abnormal foot mechanics can exacerbate the issue. Addressing bunions early through conservative measures such as proper footwear, orthotics, or padding can help alleviate pain and prevent progression, though severe cases may require surgical intervention.
Causes of Gout
Gout is primarily caused by an excess of uric acid in the bloodstream, which leads to the formation of urate crystals in the joints, sparking intense pain and inflammation. Several factors contribute to the elevated uric acid levels and subsequent development of gout, which include:
-
Dietary Choices:
- Consumption of foods high in purines, such as red meat and seafood, can increase uric acid levels.
-
Alcohol Consumption:
- Regular intake of alcoholic beverages, especially beer, can contribute to higher uric acid levels.
-
Genetic Predisposition:
- A family history of gout can increase one’s risk of developing the condition.
-
Health Conditions:
- Certain diseases and conditions, like hypertension, obesity, and diabetes, can predispose individuals to gout.
-
Medications:
- The use of diuretics and other medications can affect uric acid concentration in the blood.
Causes of Bunions
Bunions are complex deformities with several contributing factors that can influence their development and severity. While the exact cause can vary, some key factors are commonly associated with the formation of bunions:
-
Genetic Predisposition:
- A family history of bunions can significantly increase the likelihood of developing this condition.
-
Footwear Choices:
- Tight-fitting shoes, high heels, or shoes with a narrow toe box can exacerbate the formation of bunions.
-
Foot Strain or Injuries:
- Excessive stress on the feet, injuries, or abnormalities in foot mechanics can contribute to bunion development.
-
Arthritis:
- Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can increase the risk of bunions due to joint damage and misalignment.
-
Age and Gender:
- Bunions are more common in older individuals and women, possibly due to hormonal influences and footwear styles.
How To Treat
Treating gout or bunions is crucial for maintaining overall foot health, reducing pain, and preventing potential complications that can affect mobility and quality of life. Without proper management, these conditions can lead to chronic discomfort, further joint or bone deformities, and in severe cases, impair one’s ability to perform daily activities, underscoring the importance of seeking appropriate care.
Gout
Treating gout involves a combination of medication to reduce pain and inflammation and lifestyle changes to manage uric acid levels. Medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, and corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to alleviate acute gout attacks. Long-term management focuses on dietary modifications, such as reducing purine-rich foods and alcohol intake, alongside medications that lower uric acid levels, aiming to prevent future flare-ups and reduce the risk of gout-related complications.
Bunions
Treating bunions typically starts with non-surgical methods aimed at relieving pressure on the bunion and alleviating pain. These include wearing properly fitting shoes with a wide toe box, using orthotic devices to help stabilize the foot, and employing padding or splints to reduce discomfort. For more severe cases where pain persists or daily activities are significantly impacted, surgical intervention may be considered to realign the toe, remove the bunion, and correct the underlying structural problem of the foot.
People Also Ask:
-
How Can I Tell if I Have Gout or a Bunion?
- To differentiate between gout and a bunion, note that gout typically causes sudden, intense pain and swelling at the joint, often at the base of the big toe, while a bunion forms a visible bump at the side of the big toe joint, growing over time and causing persistent pain and discomfort.
-
What does Bunion Pain Feel Like?
- Bunion pain is usually a persistent, aching discomfort localized at the base of the big toe, which can intensify when wearing tight shoes or during prolonged periods of walking or standing.
-
What Does Your Big Toe Look Like if You Have Gout?
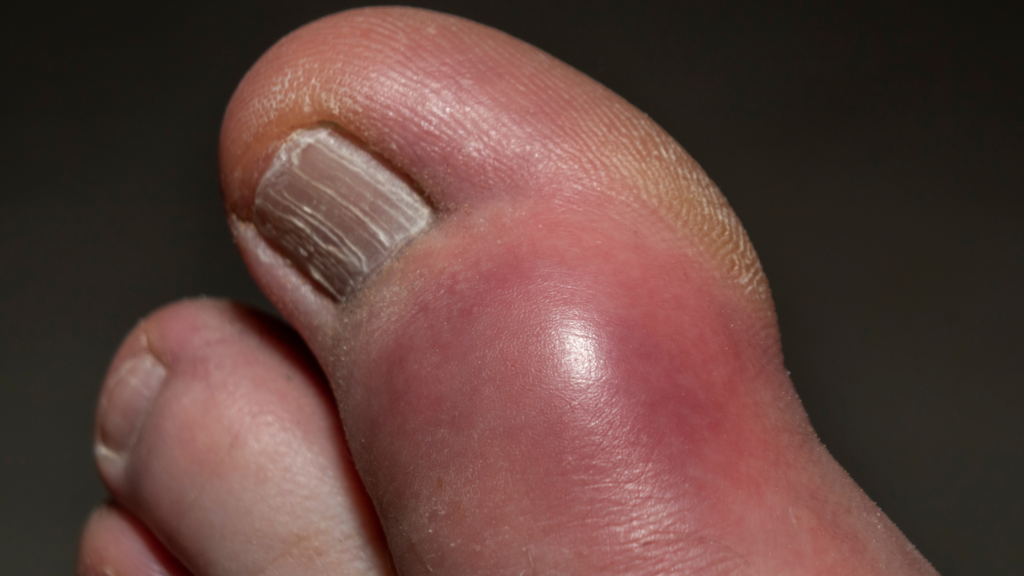
-
What Does an Inflamed Bunion Look Like?
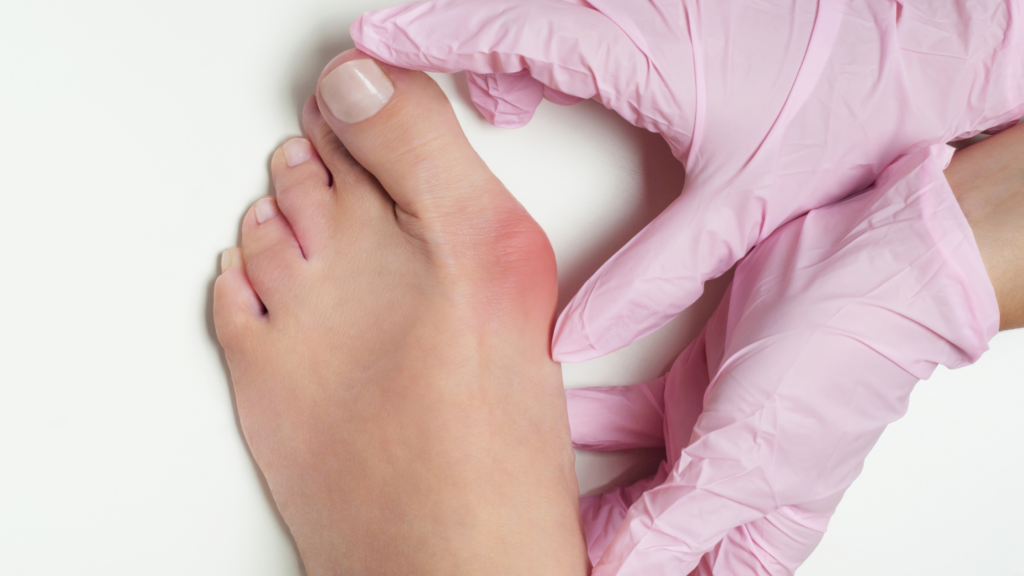
-
When Should I See a Doctor?
- You should see a doctor when you experience persistent pain, swelling, redness, or deformity in your foot, or if home remedies and over-the-counter treatments don’t relieve your symptoms, to prevent further complications and receive a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Gout and Bunions Specialist
Understanding the key differences between gout and bunions is essential for effective management and treatment of these painful conditions. Ignoring symptoms can lead to further complications, impacting your mobility and overall quality of life. If you’re experiencing persistent foot pain or suspect you have gout or a bunion, don’t wait for the condition to worsen. Contact Red Mountain Footcare today to schedule an appointment with our experts, ensuring your feet receive the best care possible and you can return to your active lifestyle without discomfort.
